Shenzhen Prechem New Materials Co., Ltd.

Comparative Performance Testing of EEP and CAC in Baking Paint Systems
Experimental Purpose and Conditions
The new solvent EEP and the traditional solvent CAC were applied in baking paint systems, respectively. By analyzing the test results in clear coat and black paint systems, and considering the differences in solvent volatility and environmental performance, a comprehensive comparison of their practical advantages and limitations was conducted.
Test Conditions: Temperature 25-27°C, Relative Humidity 50-60%.
Test Basis: Refer to GB/T 25264-2010 standard for Solvent-based Acrylic Resin Coatings.
Experiment Design and Data Analysis
Technical Parameters of Main Raw Materials:
| Name | Aparência | Ponto de inflamação | Purity | Ponto de ebulição | Viscosity @25°C, mPa.s |
| EEP (Ethyl 3-Ethoxypropionate) | Colorless, clear | 59°C | ≥99% | 169°C | 1.3 |
| CAC (Ethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether Acetate) | Colorless, clear | 47°C | ≥99% | 156°C | 1.025 |
1. Clear Coat System
Clear Coat Main Formulation:
| No. | Material | Dosage A1 | Dosage A2 | Supplier | Production Process |
| 1 | ACR8688 Acrylic Resin | 71 | 71 | Tongde | Add materials in sequence, disperse at medium speed (500 rpm) for 5 minutes. |
| 2 | CY325 Amino Resin | 18 | 18 | Cytec | |
| 3 | Xylene | 3 | 3 | Commercial | |
| 4 | n-Butanol | 3 | 3 | Commercial | |
| 5 | EEP | 5 | – | PREC | |
| 6 | CAC | – | 5 | Commercial | |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
Thinner Formulation:
| No. | Material | Dosage C1 | Dosage C2 | Supplier |
| 1 | Butyl Acetate | 90 | 90 | Commercial |
| 2 | EEP | 10 | – | PREC |
| 3 | CAC | – | 10 | Commercial |
Paint Ratio:
- Acrylic Baking Clear Coat (EEP) ratio: Main Agent A1 : Thinner C1 = 10 : 5
- Acrylic Baking Clear Coat (CAC) ratio: Main Agent A2 : Thinner C2 = 10 : 5
2. Clear Coat System Test Results and Analysis
| No. | Test Item | Test Standard | Requirement | Test Result (Acrylic Baking Clear Coat EEP) | Test Result (Acrylic Baking Clear Coat CAC) |
| 1 | Liquid Paint Odor | – | Measured | Medium-low ether-ester odor | Medium-low ether-ester odor |
| 2 | Clear Coat Viscosity, mPa.s @25.6°C | GB/T 2794-2013 | Measured | 1393.84 | 1482.51 |
| 3 | Drying Time: Through-dry, h | GB/T 1728-1979 | 140°C * 30 min | Pass | Pass |
| 4 | Film Appearance | – | Visual Inspection | Smooth, flat | Smooth, flat |
| 5 | Thickness (Flow Coating), μm | – | Measured | 43.3 | 43.5 |
| 6 | Pencil Hardness (Scratch – Zhonghua) | GB/T 6739-2006 | Measured | 3H | 3H |
| 7 | Cross-cut Test, Grade | GB/T 9286-1998 | ≤1 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | Impact Resistance, cm (Direct) | GB/T 1732-1993 | 50/50 | No cracking | No cracking |
Summary: In the clear coat system, EEP resulted in a lower application viscosity than CAC, and the film thickness is slightly lower. All other performance indicators remained comparable.
3. Black Paint System
Black Paint Main Formulation:
| No. | Material | Dosage A1 | Dosage A2 | Supplier | Production Process |
| 1 | ACR8688 Acrylic Resin | 62.39 | 62.39 | Tongde | Add materials in sequence, disperse at medium speed (500 rpm) for 5 minutes. |
| 2 | CY325 Amino Resin | 15.83 | 15.83 | Cytec | |
| 3 | Xylene | 2.65 | 2.65 | Commercial | |
| 4 | n-Butanol | 2.63 | 2.63 | Commercial | |
| 5 | EEP | 4.5 | – | PREC | |
| 6 | CAC | – | 4.5 | Commercial | |
| 7 | 9007-U Black Paste | 12 | 12 | Kedi | |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
Thinner Formulation:
| No. | Material | Dosage C1 | Dosage C2 | Supplier |
| 1 | Butyl Acetate | 90 | 90 | Commercial |
| 2 | EEP | 10 | – | PREC |
| 3 | CAC | – | 10 | Commercial |
Paint Ratio:
- Acrylic Baking Black Paint (EEP) ratio: Main Agent A1 : Thinner C1 = 10 : 5
- Acrylic Baking Black Paint (CAC) ratio: Main Agent A2 : Thinner C2 = 10 : 5
4. Black Paint System Test Results and Analysis
| No. | Test Item | Test Standard | Requirement | Test Result (Acrylic Baking Black Paint EEP) | Test Result (Acrylic Baking Black Paint CAC) |
| 1 | Liquid Paint Odor | – | Measured | Medium-low ether-ester odor | Medium-low ether-ester odor |
| 2 | Drying Time: Through-dry, h | GB/T 1728-1979 | 140°C * 30 min | Pass | Pass |
| 3 | Film Appearance | – | Visual Inspection | Smooth, flat | Smooth, flat |
| 4 | Thickness (Flow Coating), μm | – | Measured | 34.8 | 38.5 |
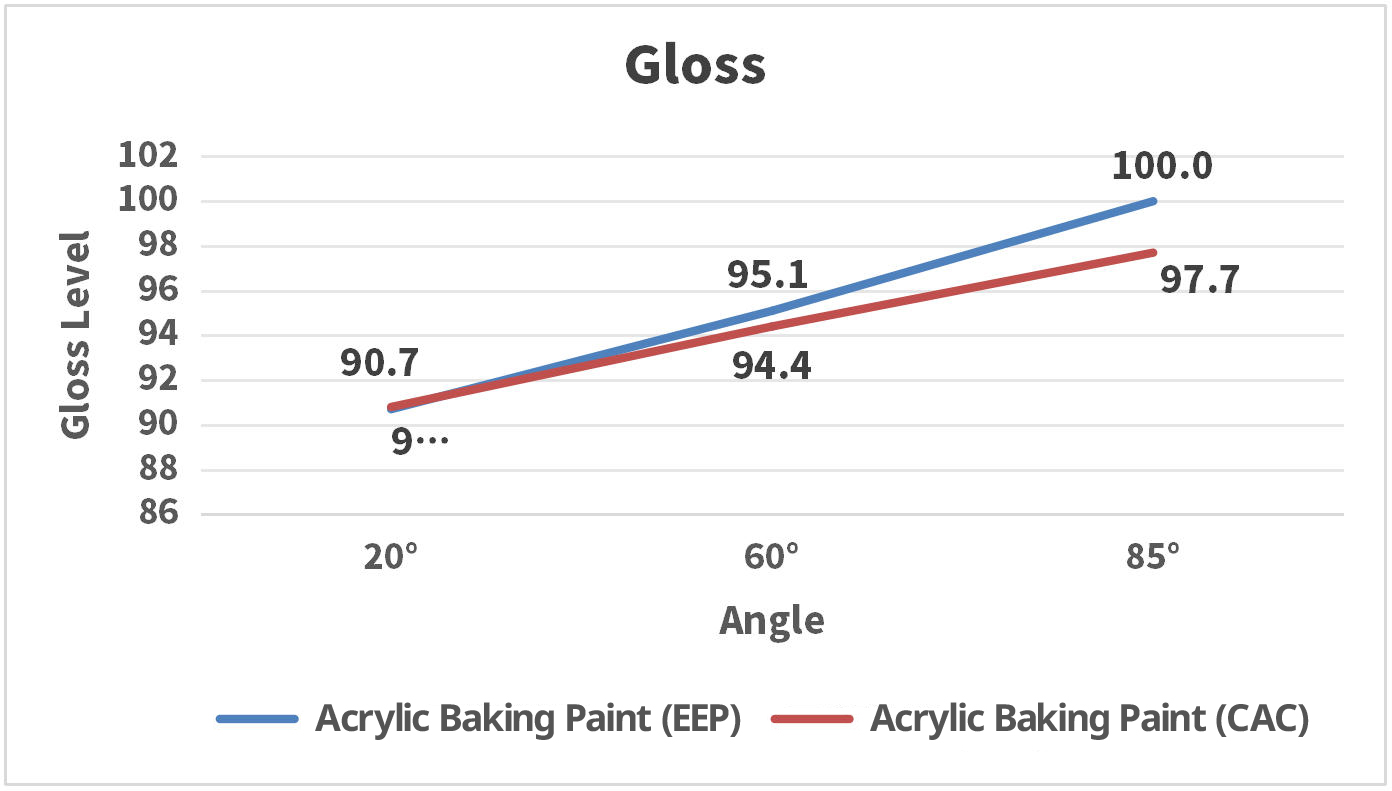
| 5 | Gloss 20°/60°/85° angle | GB/T 9754-2007 | Measured | 90.7/95.1/100.0 | 90.8/94.4/97.7 |
 | |||||
| 6 | Pencil Hardness (Scratch) | GB/T 6739-2006 | Measured | 3H | 3H |
| 7 | Cross-cut Test, Grade | GB/T 9286-1998 | ≤1 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | Impact Resistance, cm (Direct) | GB/T 1732-1993 | 50/50 | No cracking | No cracking |
| 9 | Anti-boiling Bubble Property | Panel flow-coated and immediately placed in 140°C oven for 30 mins | Few bubbles | Many bubbles | |
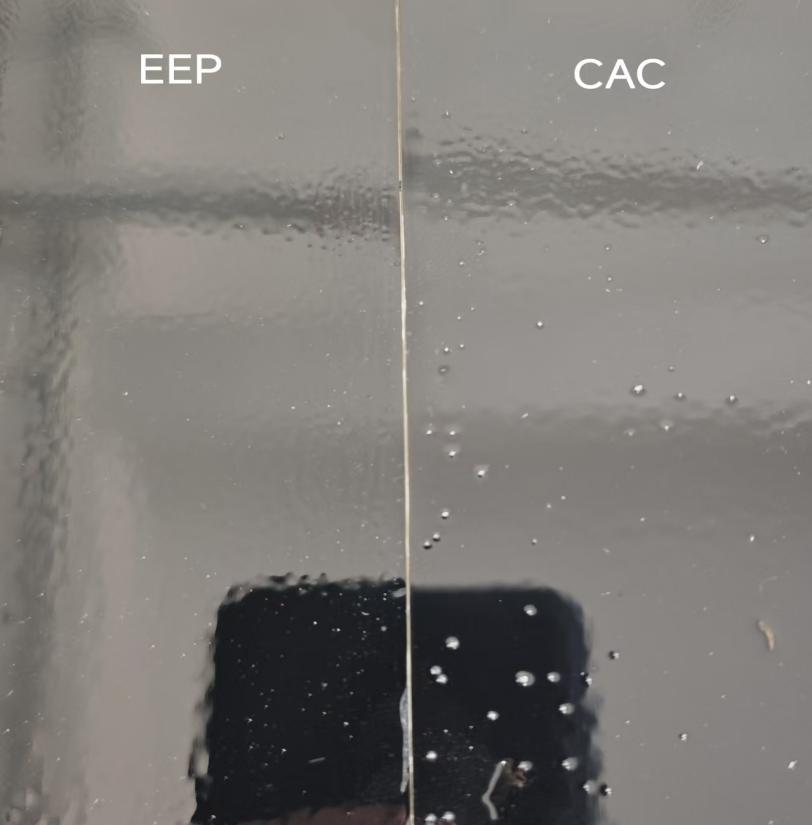 (EEP film thickness: 45.7μm; CAC film thickness: 46.5μm) | |||||
Summary: In the black paint system, EEP produced a thinner film with slightly higher overall gloss and significantly improved resistance to boiling bubbles, while other properties were essentially equivalent to those of CAC.
5. Solvent Volatility Comparison
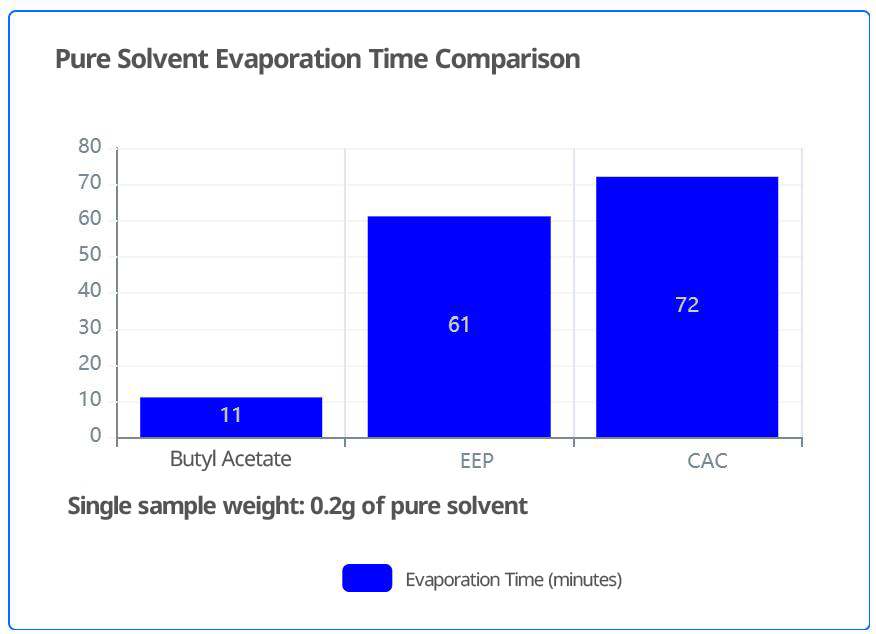
Comparative evaporation data indicate that pure EEP exhibits higher volatility than pure CAC. When mixed 1:1 with butyl acetate, the volatility of the EEP mixture is also slightly faster than that of the CAC mixture.
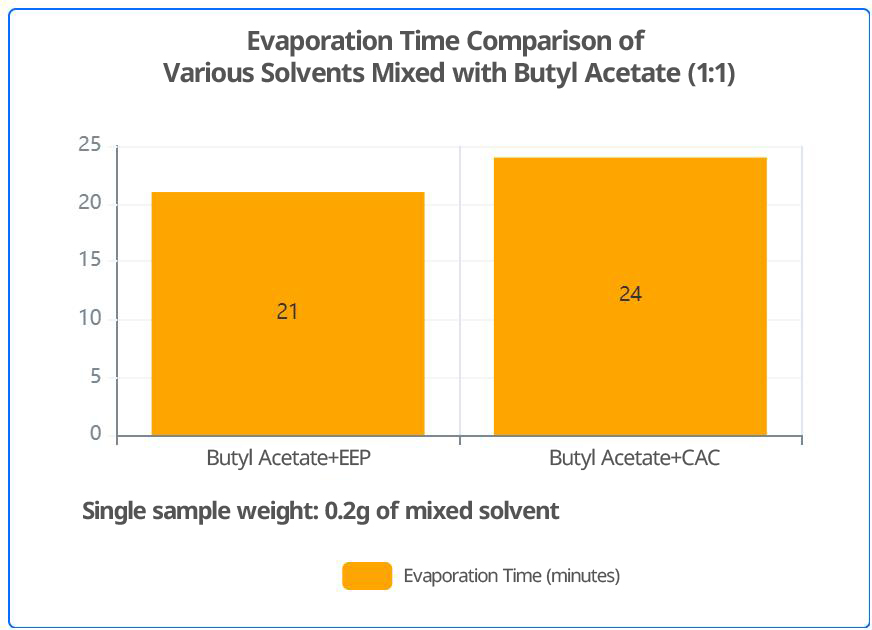
6. Environmental Performance
From an environmental perspective, EEP demonstrates clear advantages over CAC:
- Regulatory Status & Risk Level: EEP’s low VOC characteristics make it compliant with strict environmental regulations such as the EU’s REACH regulation; whereas CAC, due to its potential hazards, has been identified as an SVHC under EU REACH, and its use is strictly restricted.
- Health and Environmental Toxicity: EEP has low toxicity and low odor characteristics; in contrast, CAC has clear toxicity to humans and the environment, posing health risks with long-term exposure.
- Ecological Impact: EEP exhibits good biodegradability, whereas CAC shows limited biodegradability and may persist in the environment.
- Volatility and Emission Control: EEP’s low volatility and low VOC characteristics help reduce atmospheric pollution and the formation of photochemical smog; this makes it an ideal green choice for directly replacing non-environmentally friendly solvents like CAC and promoting sustainable industrial development.
Summary: In the black paint system, EEP produced a thinner film with slightly higher overall gloss and significantly improved resistance to boiling bubbles, while other properties were essentially equivalent to those of CAC.
Experimental Conclusion
- In the baking clear coat system, using EEP results in lower application viscosity and similar film thickness, with other performance characteristics equivalent to CAC.
- In the baking black paint system, using EEP results in higher gloss, a better anti-boiling bubble effect, and thinner film thickness, with other performance characteristics basically consistent with CAC.
- In terms of volatility, whether as a pure solvent or in a mixture with butyl acetate, EEP evaporates faster than CAC.
- In terms of environmental performance, EEP has low toxicity, low odor, good biodegradability, and low VOC characteristics; whereas CAC, due to its toxicity and poor biodegradability, has been listed as an SVHC by the EU, and its use is strictly restricted.
Overall, EEP can effectively replace CAC and other less environmentally friendly solvents in applications such as automotive OEM coatings, two‑wheeler coatings, general industrial coatings, inks, and metal baking paints.
For further details on PREC’s functional solvents, please visit: Solvente PREC EEP