Shenzhen Prechem New Materials Co., Ltd.

Comparative Application of EEP, MMP, and PMA in Polyaspartic Polyurea Resin Systems (Part 1)
Experimental Objective
To compare the solubility of novel solvents EEP/MMP versus traditional solvent PMA for polyaspartic polyurea resins, evaluating their application potential.
Experimental Análisis de datos
Test 1: Solubility of EEP, MMP, and PMA in Polyaspartic Polyurea Resin F420
Using EEP, MMP, or PMA as solvents, polyaspartic polyurea resin F420 was dissolved at solvent mass fractions of 10%, 20%, 30%, and 40%. Viscosity curves were measured to analyze solvent solubility for F420.
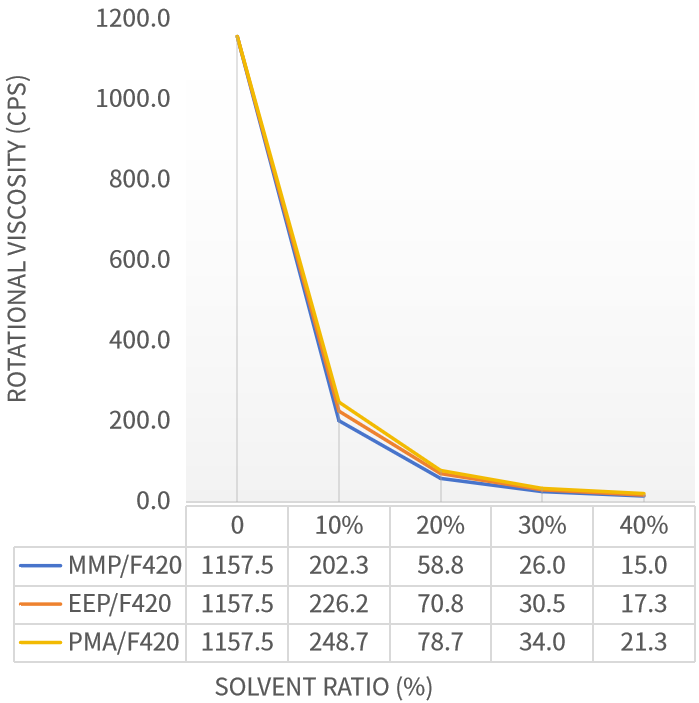
As can be seen from Figure 1, the ranking of dissolution capacity of the three single solvents for polyaspartic polyurea resin F420 is: MMP > EEP > PMA. The solubility comparison curves further illustrate that with increasing proportion (10%-40%), the viscosity curves of the novel solvents EEP, MMP and the traditional solvent PMA progressively converge, meaning the viscosity gap gradually decreases.
Test 2: Solubility of EEP, MMP, and PMA in Polyaspartic Polyurea Resin F520
Using EEP, MMP, or PMA as solvents, polyaspartic polyurea resin F520 was dissolved at solvent mass fractions of 10%, 20%, 30%, and 40%. Viscosity curves were measured to analyze solvent solubility for F520.
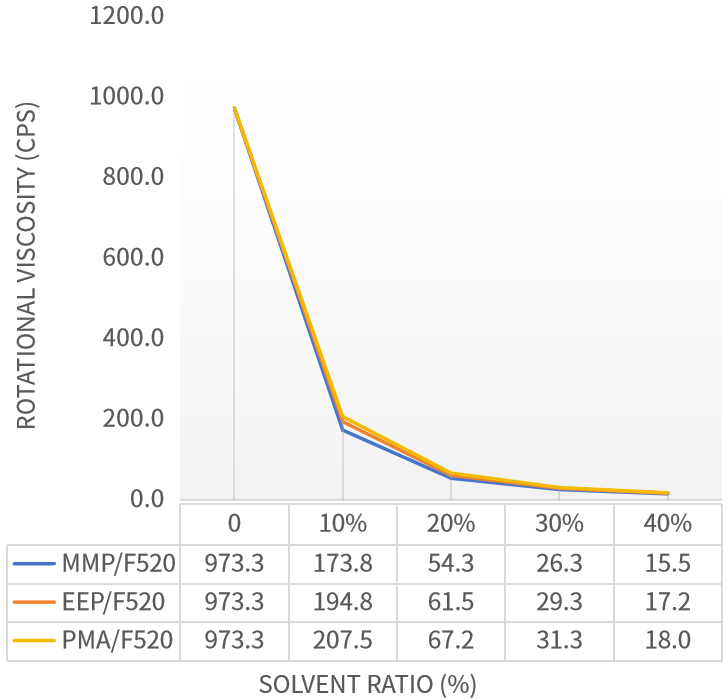
As can be seen from Figure 2, the ranking of dissolution capacity of the three single solvents for polyaspartic polyurea resin F520 is: MMP > EEP > PMA. Combined with the solubility comparison curves, it can be more intuitively observed that with increasing proportion (10%-40%), the viscosity curves of the novel solvents EEP, MMP and the traditional solvent PMA progressively converge, meaning the viscosity gap gradually decreases.
Test 3: Solubility of Composite Solvents in Polyaspartic Polyurea Resin F420
EEP, MMP, and PMA were respectively formulated into compound solvent systems with the ratio EEP/MMP/PMA : Xylene : n-Butyl Acetate = 4:3:3. These three formulated compound solvents were then used to dissolve the polyaspartic resin F420 at proportions of 10%, 20%, 30%, and 40%. Viscosity changes were tested to analyze the dissolution capacity of the compound solvents for F420.
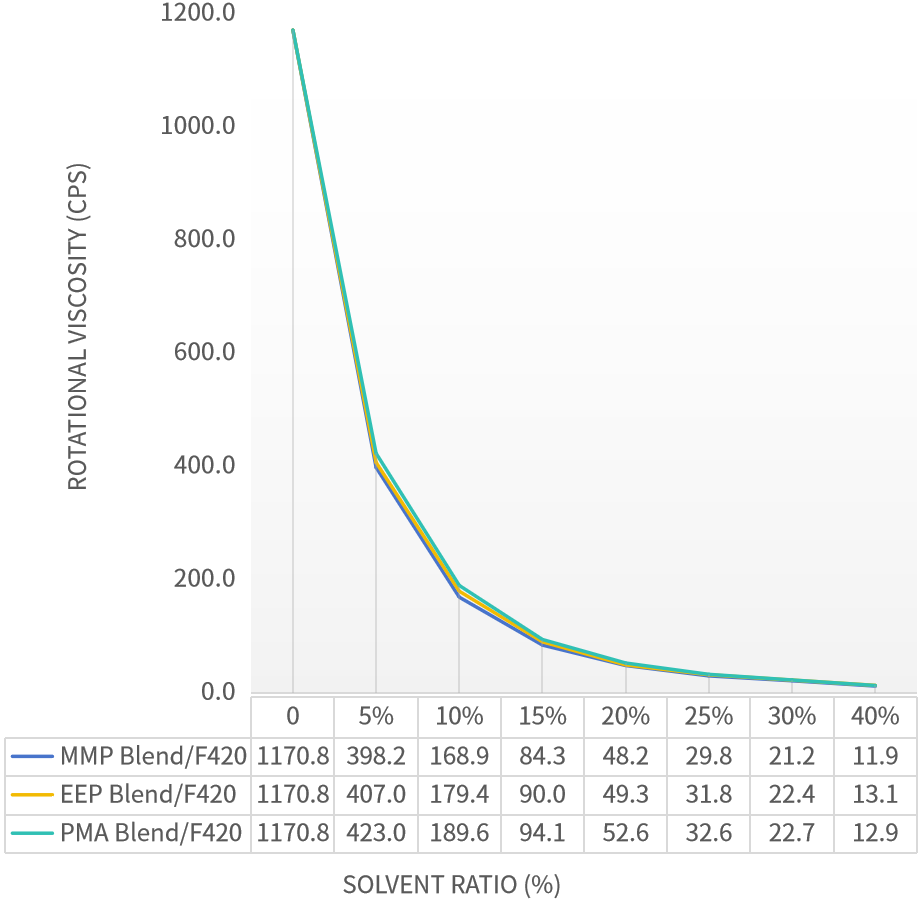
As can be seen from Figure 3, the compound solvent systems of novel solvents EEP and MMP exhibit marginally superior solubility for F420 resin compared to the traditional solvent PMA, with the solubility hierarchy being: MMP > EEP > PMA.
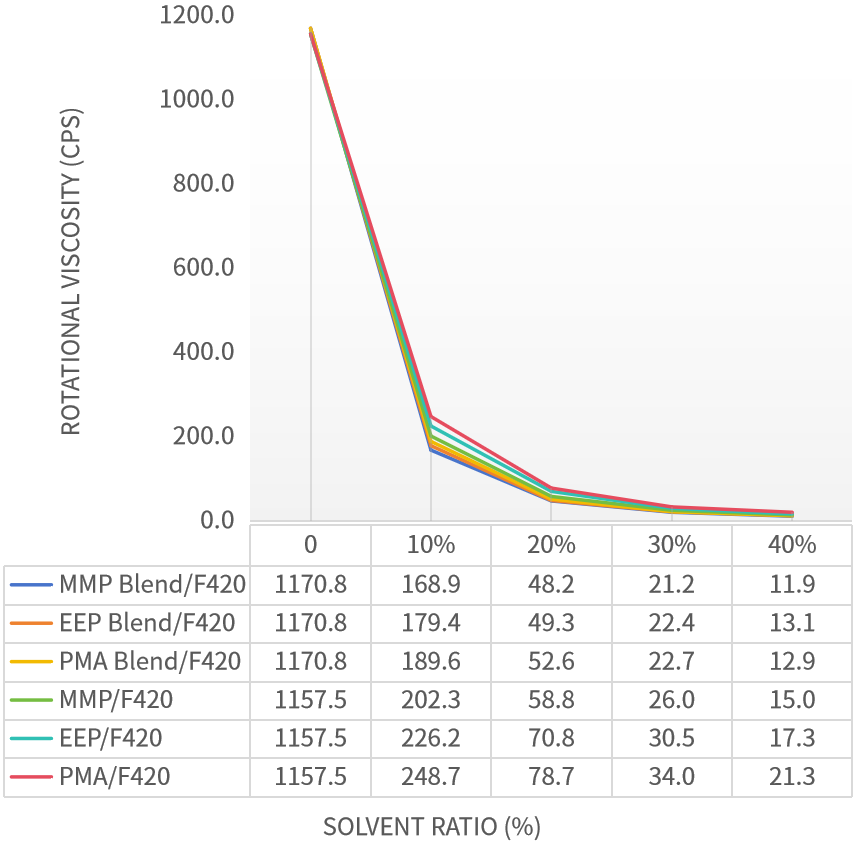
As can be seen from Figure 4, whether for the novel solvents EEP, MMP, or the traditional solvent PMA, their compound solvent systems exhibit superior solubility for F420 resin compared to their respective single solvents.
Conclusiones experimentales
- Both single and composite solvent systems of EEP/MMP show better performance than PMA in polyaspartic polyurea resin.
- Composite solvent systems significantly outperform single solvents in dissolution efficacy.
Para más información sobre disolventes funcionales, visite Disolvente PREC EEP y Disolvente PREC MMP.