Shenzhen Prechem New Materials Co., Ltd.

Environmentally Friendly MMP as a Replacement for PMA (Part 2): Solvency Comparison
Experimental Design
Compare the solvency performance of MMP and PMA for nitrocellulose, alkyd resin, and acrylic resin. Analyze their applicability in coatings by comparing water solubility.
Data Analysis
Test 1: Solvency Evaluation
1.1 Dissolving Nitrocellulose
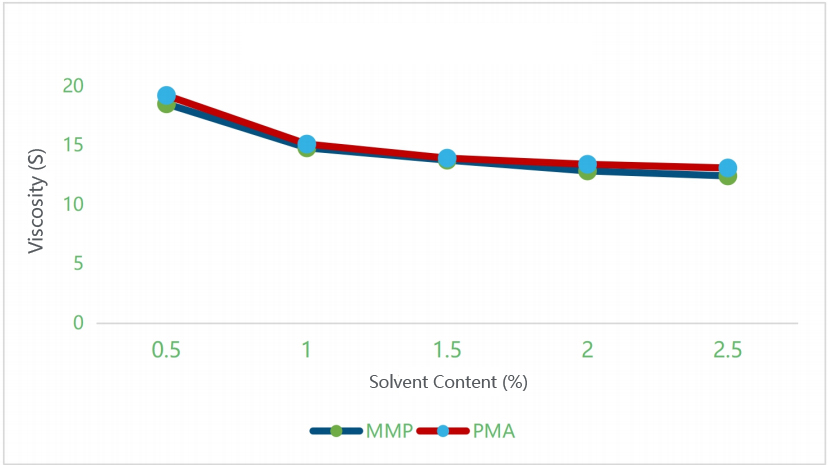
- The ratios of nitrocellulose to solvent (MMP/PMA) were set at 1 : 0.5, 1 : 1, 1 : 1.5, 1 : 2, and 1 : 2.5.
- Viscosity of each sample was measured using a Ford-4 cup.
From Figure 1, under the same solvent content, MMP achieves lower viscosity than PMA. Lower viscosity indicates stronger solvency, confirming MMP’s slightly superior solvency for nitrocellulose compared to PMA.
1.2 Dissolving 3380A Alkyd Resin
Table 1 shows that MMP produces notably lower viscosity than PMA at both 3380A alkyd resin : solvent ratios (65 : 50 and 100 : 8), confirming MMP’s stronger solvency for alkyd resin.
| MMP | PMA | |||
| 3380A alkyd resin : solvent ratios | 65 : 50 | 100 : 8 | 65 : 50 | 100 : 8 |
| Viscosity (25℃) | 12″ 75 | 5300 cps | 15″ 57 | 7600 cps |
Table 1
1.3 Dissolving AC1011 Acrylic Resin
At a 15:1 AC1011 Acrylic Resin:solvent ratio, MMP achieves lower viscosity than PMA (as shown in Table 2), demonstrating MMP’s enhanced solvency for acrylic resin.
| MMP | PMA | |
| AC1011 Acrylic Resin : solvent ratio | 15 : 1 | 15 : 1 |
| Viscosity (25℃) | 3000 cps | 3300 cps |
Table 2
Test 2: Water Solubility Evaluation
Test results: 100 g water dissolves 10 g PMA, 100 g water dissolves 66 g MMP.
MMP exhibits 56% higher water solubility than PMA.
Experimental Conclusions
The solvency of Methyl 3-Methoxypropionate (MMP) and Propylene Glycol Methyl Ether Acetate (PMA) for nitrocellulose, alkyd resin, and acrylic resin was tested. Experimental data conclusively demonstrated that MMP exhibits superior solvency compared to PMA, consistent with our hypotheses. This advantage enables MMP to reduce solvent usage, simplify formulations, and optimize leveling in coating applications.
The water solubility of MMP and PMA was also tested. MMP demonstrates significantly higher water solubility than PMA, allowing better compatibility with aqueous and resin phases in waterborne coatings. This reduces risks of stratification or precipitation, enhancing coating storage stability. Additionally, high water solubility may reduce reliance on additional co-solvents or emulsifiers, simplifying formulation design and lowering production costs.
Background
Solvents are widely used in coatings and inks to dissolve components (e.g., active agents, polymer resins, pigments) for ease of transport and application. However, solvents evaporate during film formation, releasing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. Global environmental regulations are increasingly tightening restrictions on solvent emissions, thereby driving the demand for high-solvency, low-toxicity alternatives to minimize solvent usage.
Oxygenated solvents like glycol ethers and glycol ether esters combine ether/alcohol or ether/ester properties for broader applicability. PMA, an exemplary ether-ester solvent, is widely used in coatings. Recent advancements have introduced Methyl 3-Methoxypropionate (MMP) as a superior PMA alternative. This study compares MMP and PMA in coating applications.
For more information about functional solvents, please visit: PREC MMP Solvent.