Shenzhen Prechem New Materials Co, Ltd.

Environmentally Friendly MMP as a Replacement for PMA (Part 3): Other Performance Comparison
Conception expérimentale
By comparing Methyl 3-Methoxypropionate (MMP) and Propylene Glycol Methyl Ether Acetate (PMA) in terms of tolerance to non-polar solvents, thermal stability, and hydrolysis resistance, this study analyzes their performance differences in formulation systems.
Analyse des données
Test 1: Tolerance Test for Non-Polar Solvents
1.1 Nitrocellulose + n-Heptane Test
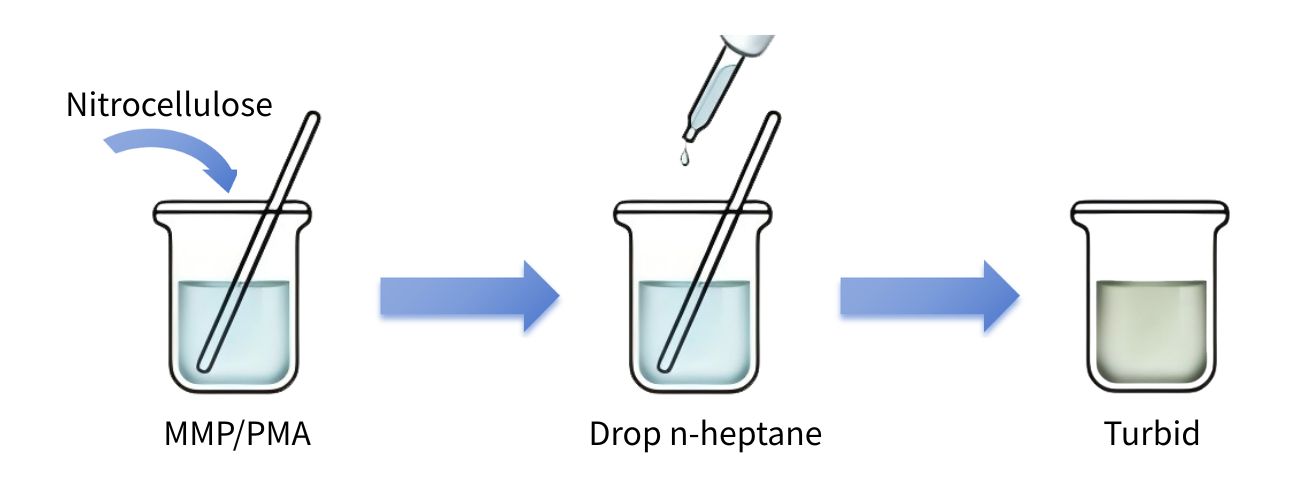
Equal masses of MMP and PMA samples were mixed with nitrocellulose (1:1 ratio), dissolved under stirring, then slowly titrated with n-heptane. The weight of n-heptane added at the onset of turbidity was recorded.
Result: MMP tolerated 35% n-heptane vs. PMA’s 15%.
1.2 Nitrocellulose + Toluene Test

Same procedure as 1.1 using toluene.
Result: MMP tolerated 76% toluene vs. PMA’s 30%.
1.3 Summary
MMP exhibited 2.3× higher tolerance to n-heptane and 2.5× higher tolerance to toluene than PMA, indicating superior compatibility with non-polar solvents. This enables higher proportions of low-cost solvents in formulations, potentially reducing overall costs.
Test 2 : Stability Tests
2.1 Thermal Stability
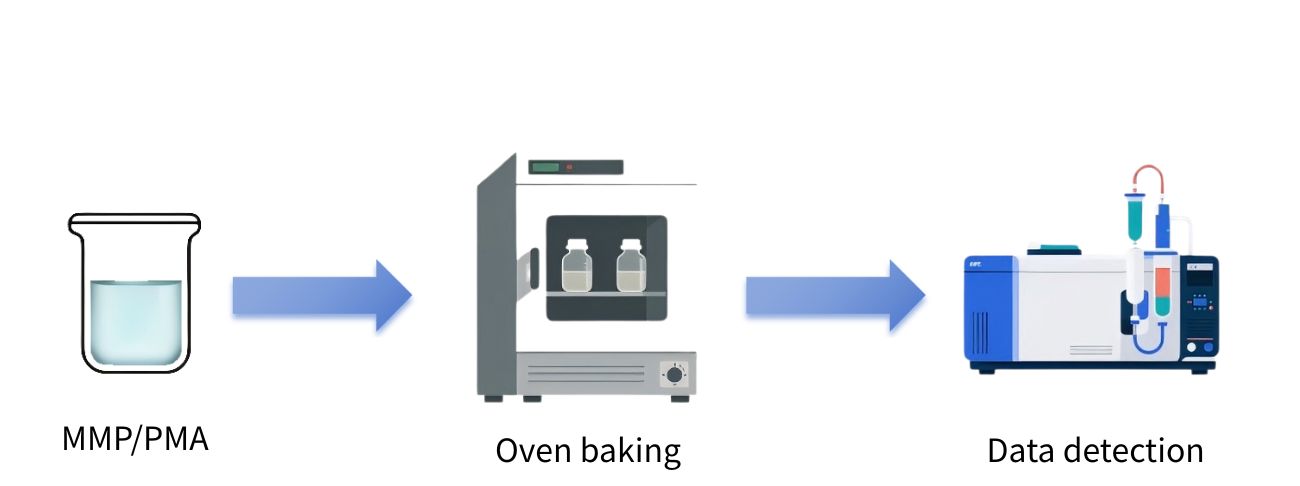
Samples were heated at 50°C, 70°C, 80°C, and 90°C for 48h and 72h.
Result: MMP and PMA showed comparable thermal stability.
2.2 Hydrolysis Test
Samples with 4% water addition and water-saturated samples were heated at 40°C for 48h.
Result:
- Both solvents suppressed hydrolysis under saturated conditions (lower acid value change).
- Under saturated conditions, MMP showed greater acid value variation than PMA.
- With 4% water addition, MMP exhibited smaller acid value change than PMA, indicating better stability. MMP demonstrates stronger water absorption but higher hydrolysis resistance with limited water.
Conclusions expérimentales
MMP showed significantly higher tolerance to non-polar solvents than PMA, providing broader formulation adaptability. Using MMP may allow higher proportions of low-cost solvents, reducing formulation costs.
Thermal stability was comparable between both solvents. Under water-saturated conditions, both inhibited hydrolysis, though MMP exhibited greater acid value variation. With limited water (4% addition), MMP demonstrated superior stability.
Contexte
Solvents are widely used in coatings and inks to dissolve components (e.g., active agents, polymer resins, pigments) for ease of transport and application. However, solvents evaporate during film formation, releasing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. Global environmental regulations are increasingly tightening restrictions on solvent emissions, thereby driving the demand for high-solvency, low-toxicity alternatives to minimize solvent usage and reduce VOC emissions.
Oxygenated solvents like glycol ethers and glycol ether esters combine ether/alcohol or ether/ester properties for broader applicability. PMA, an exemplary ether-ester solvent, is widely used in coatings. Recent advancements have introduced MMP as a superior alternative to PMA. This study compares MMP and PMA in coating applications.
Pour plus d'informations sur les solvants fonctionnels, veuillez consulter le site : PREC MMP Solvant.